The LEGO Group’s production of LEGO® bricks in the US and Canada begins in 1961 with a licensing agreement with Samsonite, the luggage manufacturer. Under the agreement, Samsonite undertakes to manufacture LEGO bricks in Denver, Colorado, on its own molding machines but with molds rented from the LEGO Group’s tooling factories in Denmark and Germany. Canadian production is to take place in Stratford, Ontario.
The JUMBO brick
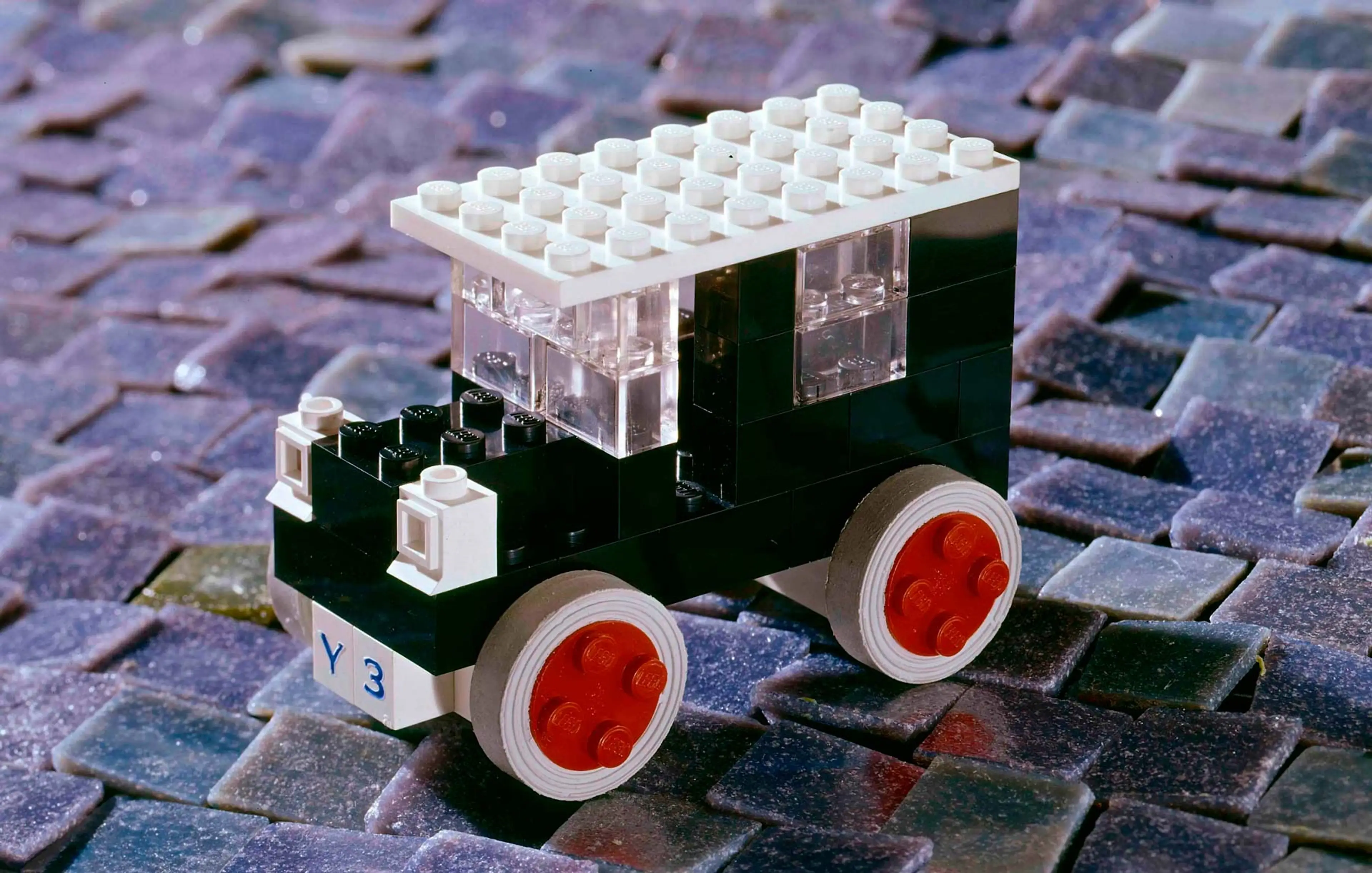
During the first half of the 1960s, the LEGO Group in partnership with Samsonite plans to manufacture and market large LEGO bricks in the US, as a supplement to the LEGO bricks already on the market.
In 1964, the “kindergarten brick”, also known as the JUMBO brick, is introduced. Just as is the case with the LEGO bricks, the molds for the JUMBO bricks are made in Denmark and sold to Samsonite, who manufactures and sells the kindergarten bricks in the US and Canada. The bricks are manufactured in Canada until 1970 and the US until 1971.

The JUMBO brick was considerably larger than a LEGO® brick
Ending the partnership
Over time, the LEGO Group is dissatisfied with the Samsonite partnership in terms of the quality of the bricks produced. Moreover, LEGO Group expectations about sale and distribution of LEGO sets is not met. In consequence, the license agreement is cancelled in ultimo 1972 and from 1973, the LEGO Group handles its own production and sale of LEGO products in the US. The agreement only applies in the US market.
The Samsonite contract remains in force in Canada until May 1988 – after which the LEGO Group establishes a sales office in Markham, Ontario.
Own production in the USA
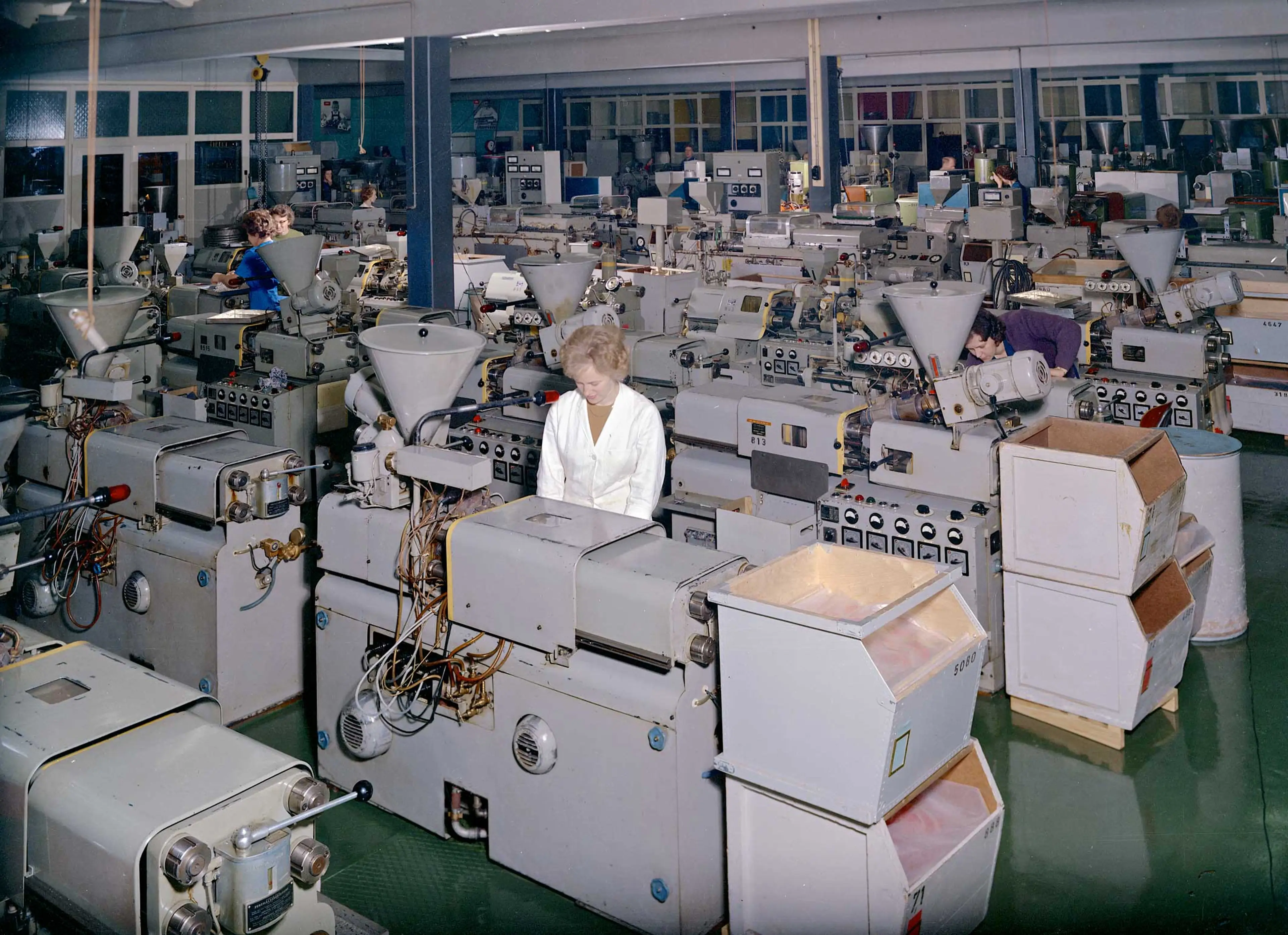
In mid-1973, the LEGO Group sets up a subsidiary in the US under the name LEGO Systems Inc. The company rents premises in Brookfield, Conn., but moves to Enfield, Conn. in 1975.

Advertisement from LEGO Systems Inc., after the partnership with Samsonite is terminated, 1973
The first LEGO factory in Enfield opens in 1975 – a packing facility for LEGO DUPLO® bricks. The elements to be packed arrive from factories in Billund, Denmark, and Baar, Switzerland – transported to the US in container ships.
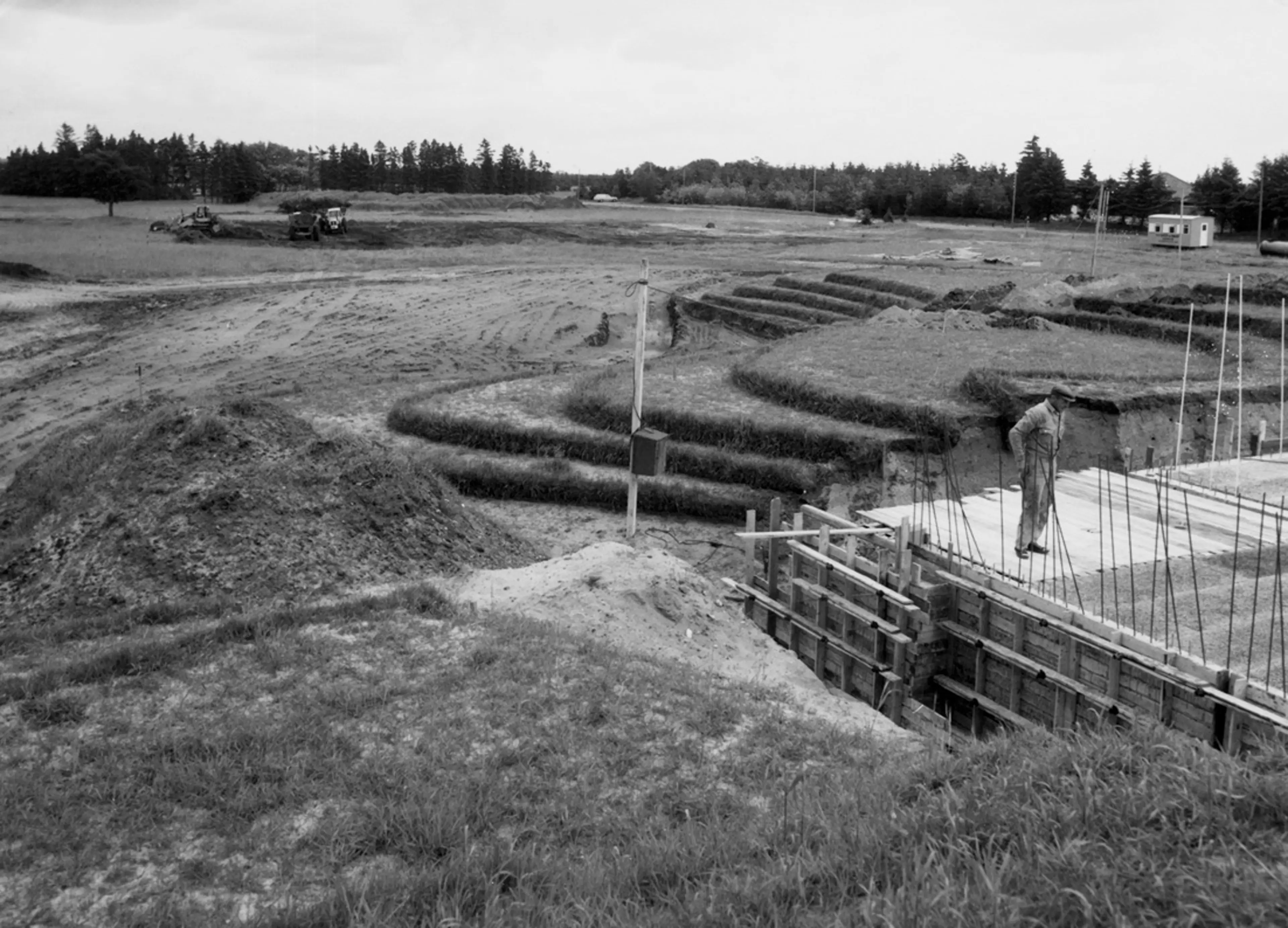
The Enfield factory is constructed as a “conversion ready” building with open steel structures which can quickly be converted from warehouse to packing, packing to production.

The new LEGO® factory in Enfield, 1975
In 1980, LEGO Systems Inc. sets up its own molding shop in Enfield, starting with 10 molding machines. The factory is equipped with state‑of‑the‑art technology. One of the features is an air‑drying system for plastic granulate, which must contain no moisture when it enters the molding machine, as the finished bricks would otherwise fail to meet the LEGO Group’s high-quality standard.
In November 2000, the LEGO Group announces its decision to close the molding plant in Enfield and in future mold LEGO bricks only in Europe. Shutting down the molding facility is a step in the LEGO Group’s plan to improve its financial results in the years ahead – preliminary accounting figures for 2000 are negative.
The Enfield packing facility now receives LEGO bricks from Europe for packing and dispatching to markets in North and South America.
The Enfield packing plant finally closes in 2007. Its activities transfer to the Flextronics factory in Juaréz, Mexico, under the austerity programme accompanying the CEO of the LEGO Group Jørgen Vig Knudstorp’s Shared Vision plan.
Setting up factory in Virginia
In 2022, the LEGO Group announces plans to invest more than US$ 1 billion to build a new LEGO® factory in Chesterfield County, Virginia. Once completed and fully operational, the 1.7 million square-foot (160,000 m2) facility will employ more than 1,760 LEGO colleagues.
The factory will be designed to operate as a carbon-neutral facility. 100 percent of its day-to-day energy needs will be matched by renewable energy generated by an onsite solar park. The site will also be designed to minimise energy consumption and use of non-renewable resources.